Nature of Sovereignty
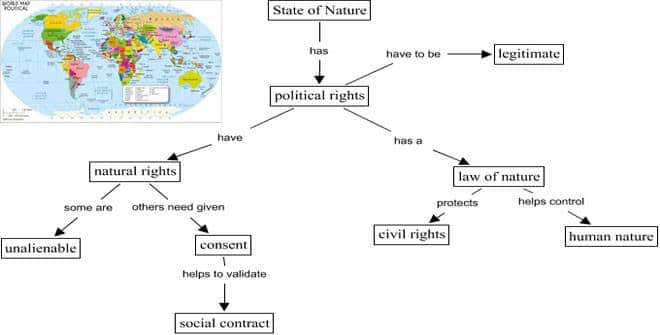
The nature of sovereignty is the defining feature that distinguishes the state from all other human associations. Sovereignty represents the supreme will and final authority within a territory—the ultimate power to command, legislate, and enforce obedience. While individuals and organizations possess collective wills, only the state enjoys the authority to override all others in cases … Read more