Influence Power And Authority
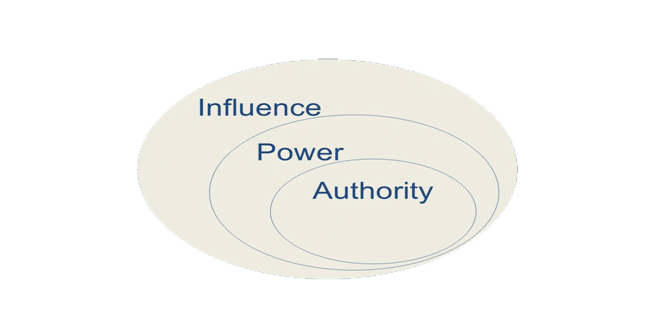
Influence, authority, and power are central to understanding how political systems function, yet they are often used interchangeably despite crucial differences. In politics, influence typically works without coercion, shaping behavior through persuasion and reputation, while power can compel compliance through force or legal authority. Authority carries legitimacy—people acknowledge the right of leaders to make decisions. … Read more